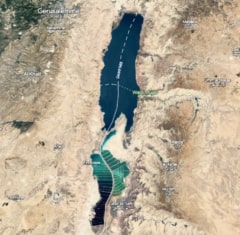
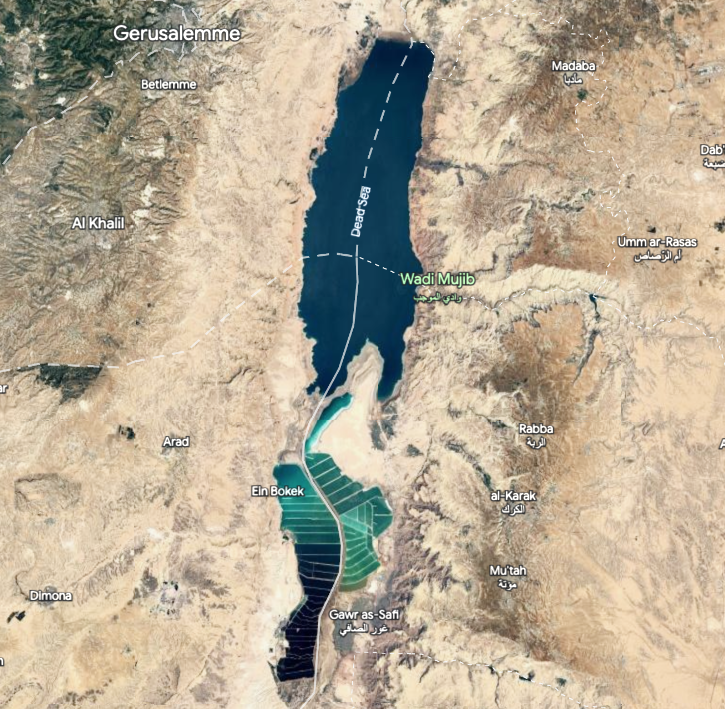
The Dead Sea is famous for its salts and the healing properties of its mud. It is the second largest saltwater lake in the world (the record is held by the Caspian Sea), shared by Israel, Jordan and the West Bank. It can give an idea of how incredibly salty it is that the average salt concentrationof its waters is almost 10 times higher than that of the oceans and seas, and floating in this lake is incredibly simple, so much so that it is almost impossible to swim normally.
Dead Sea: where it is and how it was formed
But why is it called the Dead Sea? Because the very high salinity of its waters make them inhospitable for almost every form of life, something that did not go unnoticed by the peoples who over the centuries frequented the shores of this immense lake, so large as to be called “sea” and so empty as to deserve the nickname of “dead”. “Dead” to such an extent that diving too long in its waters could become risky to health, and in fact in all bathing establishments a sign warns unsuspecting tourists of the danger that the salts of the Dead Sea represent for the eyes and ears, recommending to limit yourself to floating in the water for a maximum of 15 minutes.
Collated in the Rift Valley, a vast tectonic fault that extends from Jordan to Mozambique, Africa. Its origins are still a mystery, but the most accredited theory is that the Dead Sea was once united to the Mediterranean and that a series of tectonic movements have progressively isolated it. This geological history has meant that the Dead Sea enjoys a further record: with its 400 meters below sea level, it is the lowest point of the land.
The challenge of evaporation
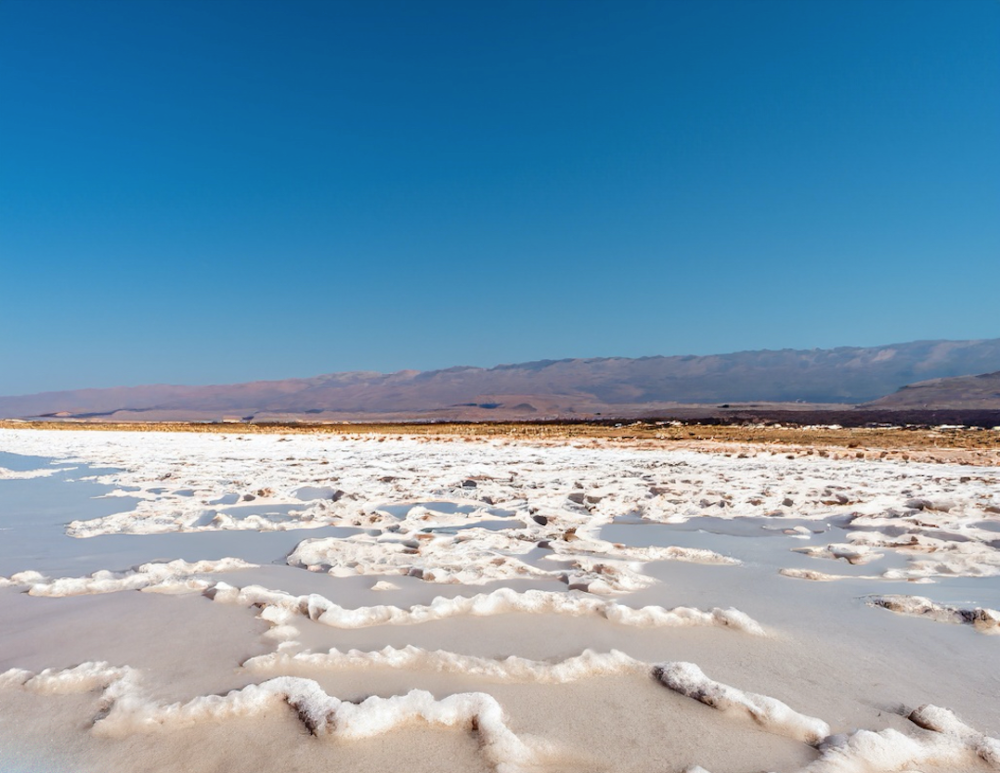
The only source of new water into the Dead Sea is the Jordan River, while, unlike most lakes, it has no outlet, making it an endorheic basin. Despite this, the Dead Sea is slowly disappearing. With increasing temperatures and arid climate, its waters are subject to strong evaporation, causing an increase in the concentration of salt in the water and a decrease in sea level. As the water level decreases, the entire ecology of the lake is threatened. Every year the level of the coast drops by a few meters, so much so that the locals remember how there was only water where roads now run.
One of the main factors contributing to its disappearance is the poor input of water into the lake. The only significant source of water for the Dead Sea is the Jordan River, but in recent decades, the river’s water flow has decreased dramatically due to the construction of dams and the intensive use of water for agricultural purposes. Without adequate water intake, the Dead Sea continues to lose level, inexorably leaving vast surfaces that were once submerged uncovered.

Dead Sea: Jordan, Israel and the West Bank. Projects and conservation efforts
Preserving the Dead Sea is a complex and urgent challenge, requiring the cooperation of all actors involved. Israel, Jordan and the West Bank have begun to work together to seek concrete solutions and projects to preserve the lake. One of the main proposals was to transfer water from the Red Sea to the Dead Sea through acanal, which would help restore the water level and preserve the salt lake.
Another proposal is to create a connecting channel from the Mediterranean that exploits its elevated position to transport the water necessary to prevent the disappearance of this lake.
However, these solutions involve technological and financial complexity, and the challenge of preserving the Dead Sea remains enormous. Especially because, as you can easily imagine, these projects would require perfect collaboration between the political entities affecting the area: Jordan, Israel and the West Bank. It is therefore essential to raise public awareness and involve the international community as much as possible to protect this unique natural treasure and ensure its survival.
Environmental and Socio-economic Impacts
The disappearance of the Dead Sea would have devastating impacts on the region’s ecosystem and the lives of local communities. Just to name a few:
- Reduction of biodiversity: The high salinity of these waters limits life, but some species of bacteria and algae have learned to survive. Its disappearance could lead to the extinction of these extraordinarily adapted life forms.
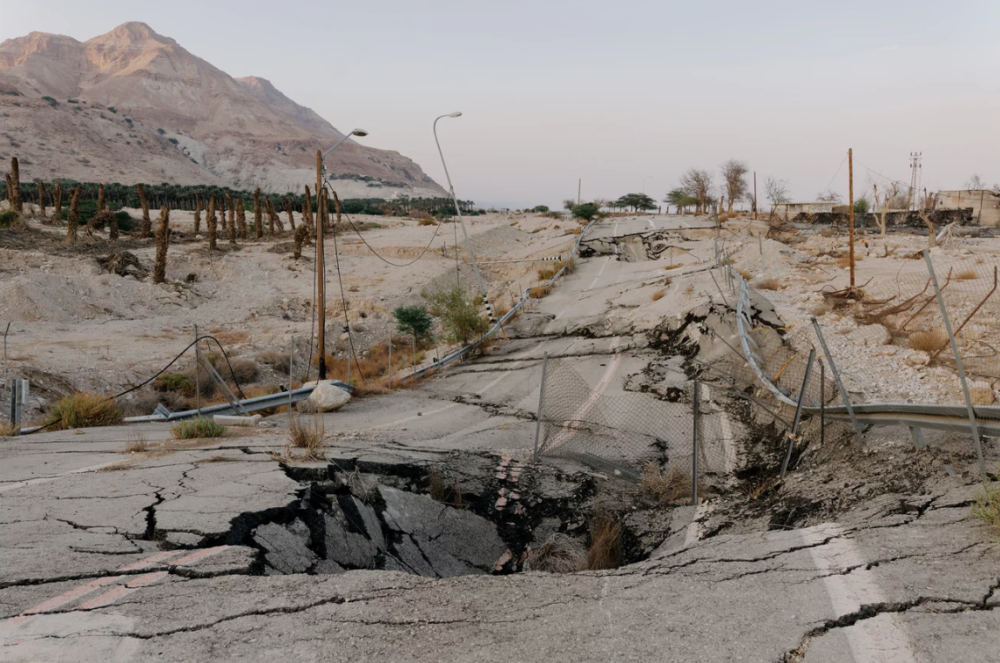
- Risk of collapse:The depression that hosts the Dead Sea could suffer continuous collapses and deformations due to the extraction of salts and the lowering of the water level. The continuous risk of collapse has meant that several roads built to reach the bathing establishments have been closed for safety reasons, causing the abandonment of several of these structures.
- Economic impacts: it is a tourist destination that attracts people from all over the world every year. As a result, hotels, bars and beach clubs employ thousands of people and benefit local economies. The progressive lowering of its coasts means that these establishments have to be abandoned, ending up being too far from the shore. Finally, a total disappearance of the Dead Sea would have very serious economic consequences for all the economies of the surrounding countries.

The Dead Sea is a wonder of nature and a unique historical and cultural testimony. However, its disappearance is a real and imminent threat. It is vital to act decisively to preserve this natural treasure for future generations and to ensure that it continues to enchant its visitors for many years to come.
Only through a joint commitment of the nations involved and the international community can we hope to save and protect its inestimable ecological, historical and cultural value.
By: Jacopo Battistini